Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MySQL CASE expression to add if-else logic to queries.
MySQL CASE expression is a control flow structure that allows you to add if-else logic to a query. Generally speaking, you can use the CASE expression anywhere that allows a valid expression e.g., SELECT , WHERE and ORDER BY clauses.
The CASE expression has two forms: simple CASE and searched CASE .
Note that MySQL has a CASE statement that you can use only in stored programs such as stored procedures, stored functions, events, and triggers, which is not the CASE expression covered in this tutorial.
The following illustrates the syntax of a simple CASE expression:
CASE value WHEN value1 THEN result1 WHEN value2 THEN result2 … [ELSE else_result] ENDCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax, CASE matches the value with the value1 , value2 , etc., for equality and return the corresponding result1 , result2 ,… If the value does not equal to any value1 , value2 , … CASE returns the result in the ELSE clause if the ELSE clause is specified.
The CASE compares the value with values in the WHEN clauses for equality, you cannot use it with NULL because NULL = NULL returns false.
The following shows the syntax of a searched CASE expression:
CASE WHEN expression1 THEN result1 WHEN expression2 THEN result2 … [ELSE else_result] ENDCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax, the CASE evaluates expressions specified in the WHEN clauses. If an expression evaluates to true. CASE returns the corresponding result in the THEN clause. Otherwise, it returns the result specified in the ELSE clause. In case the ELSE clause is not available, then the CASE expression returns NULL .
The CASE expression returns a result whose data type depends on the context where it is used. For example, if the CASE expression is used in the character string context, it returns the result as a character string. If the CASE expression is used in a numeric context, it returns the result as an integer, a decimal, or a real value.
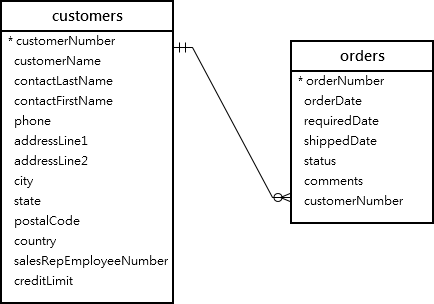
See the following orders and customers tables:

The following statement returns the customers and their orders:
SELECT customerName, COUNT(*) orderCount FROM orders INNER JOIN customers USING (customerNumber) GROUP BY customerName ORDER BY COUNT(*);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)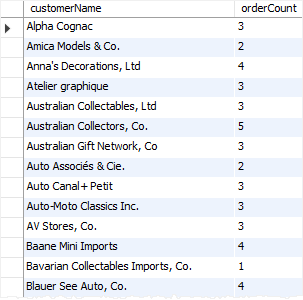
This example uses the CASE expression in the SELECT clause to return the type of customers based on the number of orders that customers ordered:
WITH cte AS ( SELECT customerName, COUNT(*) orderCount FROM orders INNER JOIN customers USING (customerNumber) GROUP BY customerName ) SELECT customerName, orderCount, CASE orderCount WHEN 1 THEN 'One-time Customer' WHEN 2 THEN 'Repeated Customer' WHEN 3 THEN 'Frequent Customer' ELSE 'Loyal Customer' end customerType FROM cte ORDER BY customerName;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)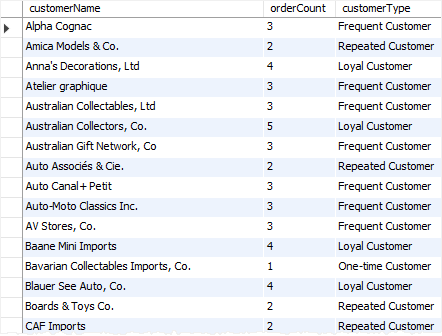 MySQL CASE expression with SELECT clause" width="442" height="336" />
MySQL CASE expression with SELECT clause" width="442" height="336" />
The following example uses the CASE expression to sort customers by state if the state is not NULL , or sort the country in case the state is NULL :
SELECT customerName, state, country FROM customers ORDER BY ( CASE WHEN state IS NULL THEN country ELSE state END);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)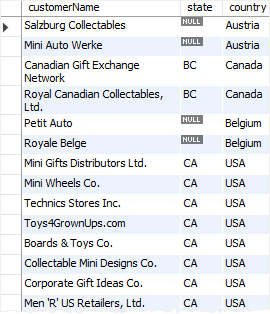 MySQL CASE expression with ORDER BY clause" width="270" height="314" />
MySQL CASE expression with ORDER BY clause" width="270" height="314" />
The following example uses the CASE expression with the SUM() function to calculate the total of sales orders by order status:
SELECT SUM(CASE WHEN status = 'Shipped' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS 'Shipped', SUM(CASE WHEN status = 'On Hold' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS 'On Hold', SUM(CASE WHEN status = 'In Process' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS 'In Process', SUM(CASE WHEN status = 'Resolved' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS 'Resolved', SUM(CASE WHEN status = 'Cancelled' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS 'Cancelled', SUM(CASE WHEN status = 'Disputed' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS 'Disputed', COUNT(*) AS Total FROM orders;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
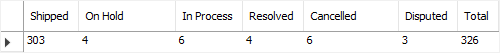 MySQL CASE expression with aggregate function example" width="500" height="53" />
MySQL CASE expression with aggregate function example" width="500" height="53" />
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the MySQL CASE expression to add if-else logic to the queries.